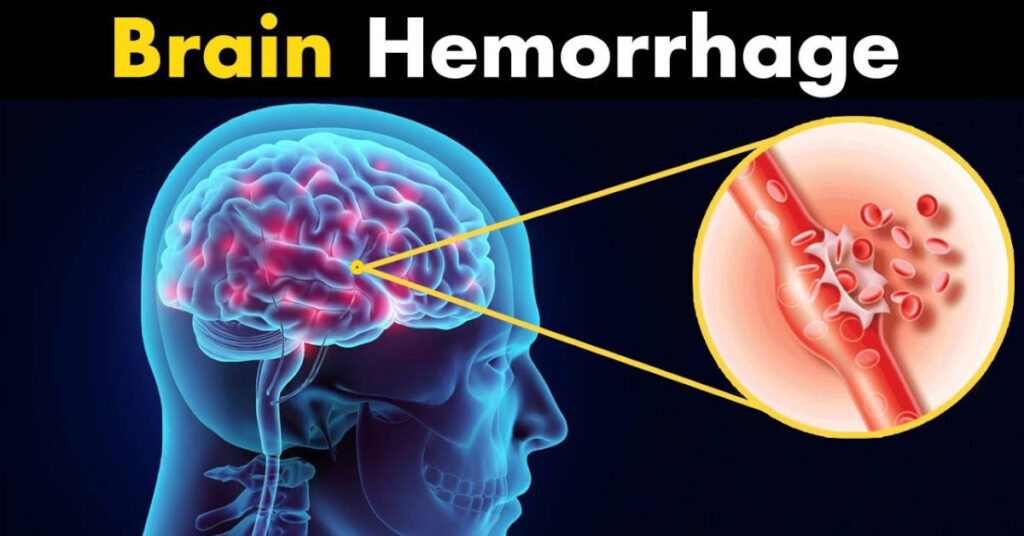
A brain haemorrhage occurs when there is bleeding either inside the brain or in the surrounding area. The reasons for brain haemorrhage are quite a few.
They include hypertension or high blood pressure, drug abuse, trauma and leaking blood vessels. A brain haemorrhage that involves bleeding inside the skull area is known as an intracranial haemorrhage. When there is bleeding inside the brain, it is known as intracerebral haemorrhage.
A haemorrhage that occurs between the brain covering and the brain tissue is known as subarachnoid haemorrhage. A situation of a subdural hematoma that is below the dura (tough covering) and epidural hematoma that is above the dura (tough covering) happens where there is blood clotting between the brain and the skull.
An epidural or subdural hematoma can occur because of trauma or because of an accident (usually a fall).
A brain haemorrhage can occur when over the passage of time there is continuous increasing blood pressure against the artery walls.
This happens during high blood pressure and can cause a rupturing of the arterial walls. Sometimes prescription medications can contribute to brain haemorrhage as well.
Drug abuse overtime also weakens the artery walls. The symptoms of a brain haemorrhage include headache (throbbing pain as a result of rupturing of an aneurysm), vomiting, nausea, numbness, changes in vision, trouble swallowing, seizures, loss of consciousness; balance and coordination, trouble with reading or writing and lethargy.
Haemorrhage which is a life threatening condition involving internal bleeding in the brain, are of three different types depending upon the location. These are such as:-
* Epidural hematoma.
* Subdural hematoma.
* Subarachnoid hematoma.
* Intracerebral hematoma.
Hemorrhage i.e internal bleeding is the condition of a medical emergency which is associated with some kind of signs and symptoms.
However, the first sign accompanying the hemorrhage is the sudden fall in the blood pressure of the individual, followed by a huge decrease in body temperature. Tachycardia, loss of consciousness, anxiety, confusion, weak pulse and dizziness occur in continuation.
Brain hemorrhage is caused due to a localized bleeding in the brain tissues caused by rupturing of an artery . The factors responsible for such conditions may include head trauma, high blood pressure, liver disease, brain tumors and blood related disorders such as Hemophilia and sickle cell anemia.
When brain hemorrhage occurs, arteries supplying blood to the brain tissues rupture which results in an interrupted blood flow to the tissues, followed by pooling of blood in the brain.
This leads to a cut in the oxygen supply to the tissues there, causing the brain cell to die. The condition may be fatal in some cases.
In case of brain haemorrhage, it is necessary to seek immediate medical treatment in the form of surgery. However, the type of surgery will depend on the age of the patient, his health condition in total and the intensity of damage caused to the brain and the location of the damage.
The decompression surgery helps to relieve the pressure possessed by the brain. A neurosurgeon will skilfully remove the pooled blood and also repair the damage that has been inflicted on the brain. If the hematoma is drained then, size of the pooled blood is reduced and the patient can get relief from his/her pain.
In order to do this the doctor can perform craniotomy or open surgery; In this surgery, the surgeon will partially remove a part of the skull and perform an open surgery in order to drain the hematoma. In the process he will also drain the blood vessels that have ruptured. This surgery is performed only when the hematoma has become very large.
In the Simple aspiration surgical method the surgeon will with the help of a needle make a hole in the skull in order to drain the hematoma. The difficulty of this surgery lies in locating the very source of bleeding.
The endoscopic evaluation method is similar to the simple aspiration method with the only difference being in the use of an endoscopic or camera in order to locate the position of the hematoma. In the stereotactic aspiration method a CT (computed tomography) along with suction tool will be used for locating and draining the hematoma respectively.
Hemorrhage, referred to as internal bleeding, needs to undergo treatment as earliest as possible as it is an emergency condition. If left untreated or in case of delayed treatment, it may prove fatal or lead to complications which include paralysis, coma, seizures, organ failure and external bleeding.
The side effects one can encounter after going through a craniotomy surgery includes bleeding, brain damage, damage to the facial muscle/ sinuses/ head pin, adverse reaction to anaesthetic and infection of bone flap.
The post-treatment guidelines of a brain haemorrhage surgery depends on a number of factors.
An aneurysm that leads to a subarachnoid haemorrhage may require the patient to be held back in the hospital for at least two weeks so that he may be monitored for the possibility of a cerebral vasospasm.
For patients who did not suffer a rupturing of the aneurysm, recovery time is quicker and less troubling. Such patients may be let out of the hospital within a few days time and they can resume their daily activities once again.
For patients who went through a craniotomy surgery (clip ligation of the aneurysm), they will be held back further for a few more days in the hospital even after being let out of the intensive care unit.
After being discharged such patients can resume their normal daily activities but should take precaution to abstain from any intense activity that can put a pressure or a strain on the self.
The patients are also asked to visit the doctor from time to time as a follow up protocol.
The recovery time for a craniotomy surgery or any other brain haemorrhage takes about 4-6 weeks to heal completely.
Brain hemorrhage is a medical emergency that needs to be followed by the treatment, which depends upon cause, location and severity of the hemorrhage. Starting with the diagnostic tests such as CT scan and MRI, surgeries are performed to control the swelling and internal bleeding.
It is then followed by certain medications including analgesics, corticosteroids, osmotic and anticonvulsant drugs.
Brain hemorrhage is an emergency medical condition followed by surgeries and medications. Recovery totally depends upon the severity of the hemorrhage including size and extent of the swelling.
Though recovery is quite possible in some cases depending on factors like post-surgery care as well response of the body towards treatment, complications such as stroke, paralysis and seizures may occur. Death too happens in some cases
People who experience bleeding in certain regions of the brain or those with an elevated initial bleeding stage stand at the risk of dying.
Over the passage of time, with required therapies and medications patients who suffered a brain haemorrhage can slowly go back to their normal daily functions.
In other cases, post-surgery, patients can continue to suffer from headaches, memory retention problems and seizures.